Introduction
ISO 27001 compliance entails proving that an organization’s information security management system (ISMS) aligns with the standard’s requirements. Achieving compliance requires undergoing an audit process where an independent third-party assessor evaluates the organization’s ISMS against said standard.
The assessor examines the organization’s policies, procedures, and controls, as well as its risk assessment and risk remediation processes, to ensure they meet the standard’s requirements. If the assessor concludes that the ISMS complies with the standard, the organization receives a certificate confirming its compliance. This certification formally acknowledges that the organization has an effective ISMS in place to safeguard its sensitive information.
According to Afnor, the number of valid ISO 27001 certificates increased from 36,000 in 2019 to around 58,000 in 2021, underscoring the growing significance of information security controls in businesses globally.
In 2022, the first update of ISO/IEC 27000 since 2013 was released, yet questions about cybersecurity assessments and requirements persist.
This article covers all aspects of penetration testing within the context of ISO 27001 compliance, providing your organization with clear and informed guidance for hiring penetration testing services for your audit.
What Is ISO 270001 Compliance?
ISO/IEC 27001 is arguably the most well-known information security standard. It provides a framework for an organization’s information security management system (ISMS), creating guidelines and requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving information security.
The standard adopts a risk management approach, helping organizations identify, assess, and prioritize risks to their sensitive information, and implement controls to mitigate those risks to an acceptable level. ISO 27001 specifies the necessary components of an ISMS, including policies, procedures, and controls, to safeguard sensitive information.
Achieving ISO 27001 compliance is a necessary step for a company in terms of data security and information security policies. A certified organization is better equipped to protect customer data and prevent data breaches, as well as mitigate them following any breaches. It can demonstrate to clients and business partners that a business has robust and audit-able security processes, thereby gaining their confidence and facilitating business deals where risk assessments and regulation compliance are critical.
What is an ISO 270001 Penetration Test?
ISO 27001 penetration testing is a comprehensive assessment aimed at evaluating the security of systems, applications, networks, cloud environments, or entire organizations. This type of test is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that security controls meet the standards established by the ISO 27001 norm. By simulating real-world cyber-attacks, penetration testing helps organizations pinpoint weaknesses, upgrade their security posture, and comply with ISO 27001 requirements.
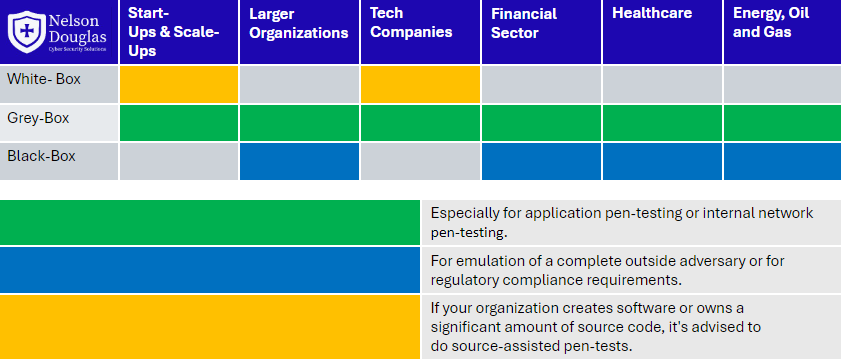
Most professional info-sec firms discourage tests exclusively based on a black box approach unless the threat model and level of adversary your company wants to emulate is at a very high aggression level. Grey-box is preferred for most ISO 27001 penetration testing engagements.
Is Penetration Testing a Requirement for ISO 27001?
No, not even with the ISO/IEC 27001:2002 update. However it’s still highly advised that pentesting be carried out as a part of an organization’s risk assessment, internal audit and risk management process. An example of this would be A.12.6.1 Management of technical vulnerabilities, stating;
- Information about technical vulnerabilities of information systems being used shall be obtained in a timely fashion, the organization’s exposure to such vulnerabilities evaluated and appropriate measures taken to address the associated risk.
Another example would be A.14.2.8 System security testing, which states;
- Testing of security functionality shall be carried out during development.
Its important to note ISO 27001 combines A.14.2.9 and A14.2.8 into a new control names A8.29 Security testing in development and acceptance. A custom ISO27001 pentest covers both A.12.6.1 and A.8.29 and provides a way to show compliance with technical vulnerability management as outlined in Annex A of ISO 27001. Penetration testing using this framework specigically looks to identify technical security vulnerabilities and demonstrates the impact and likelihood of various attack scenarios. Security testing brings an org an additional layer of assurance that they’re correctly implementing infosec controls within their networks and environment as well as having evidence of compliance if and when needed.
What is the Average Duration of ISO 27001 Penetration Testing?
The usual duration of an ISO 27001 penetration test ranges from around 5 to 30 days, depending on the size and scope of the assessment. Security testing for large and complex environments can extend over several weeks. This has been our observation for most penetration tests where ISO 27001 compliance is the primary objective.
We suggest caution when dealing with penetration testing providers that offer “fast and cheap” tests lasting only one to three days. Such assessments are often conducted almost entirely with automated scanners or, at best, follow a standard checklist without incorporating a “hacker mindset” or creativity. Consequently, there is a high risk of missing vulnerabilities and/or entire attack vectors, leaving your organization with a false sense of security.
A general guideline is that any penetration test for ISO 27001 that takes less than 40 hours for a small to medium-sized scope (e.g., a web application or a small network) is likely insufficient. This time frame doesn’t allow for a thorough manual examination of an org’s systems and a comprehensive exploration of all potential attack vectors.
Does ISO 27001 Require Vulnerability Scanning?
ISO 27001 doesn’t specifically mandate vulnerability scanning for compliance purposes. Similar to penetration testing, the type of automated security assessment isn’t a strict requirement.
However, much like pentesting, vulnerability scanning can be utilized to enhance your audit and meet the requirements specified in A.12.6.1 (managing technical vulnerabilities).
How Do You Define the Scope of an ISO 27001 Penetration Test?
The scope of a pentest is decided through collaboration between the client’s team (i.e. compliance officers, internal audit, IT personnel, etc) and the external auditor. Together, they define the systems, networks, databases, or applications to be assessed and the types of security testing to be conducted.
Based on our experience, organizations executing an ISO 27001 audit generally include the following elements in their penetration testing scope:
- The organization’s flagship product, for example, an SaaS platform.
- Web-facing server infrastructure, often cloud-hosted.
- The org’s internal network, servers, and key infrastructure, such as Kubernetes clusters and Active Directory.
- APIs (REST, GraphQL, microservices and legacy web services).
- Security testing of mobile applications where necessary.
- Any administrative panel or back-end systems supporting (as an example) the user-facing SaaS.
Often, organizations perform penetration tests in a staging environment to avoid potential disruptions to production systems. As long as the staging environment closely mirrors the production setup, this approach is acceptable and widely used. However, it is recommended to consult with the auditor before initiating a pentest to ensure they approve of this methodology.
What are Some of the Recommended Pentesting Methodologies?
Since ISO 27001 does not provide specific guidelines for penetration testing or the processes to be employed, organizations often have discretion in their approach.
However, based on our experience, several widely recognized methodologies are often used for compliance-related penetration testing. One of the most prevalent is the OWASP Top 10, which covers the most common security threats for web applications, APIs, mobile, and IoT, making it applicable for many organizations.
Other commonly used methodologies include OSSTMM and PTES, which extend beyond application security to cover network security as well. Additionally, SANS 25 (a less popular option) and NIST 800-115 can also be applied in compliance testing.
How Much Does an ISO 27001 Penetration Test Cost?
The cost of a penetration test service for ISO 27001, conducted by a reputable and accredited cybersecurity firm, typically ranges from £6,000 to £20,000 for a small to medium-sized scope (e.g., a few dozen IP addresses and a handful of web applications/APIs).
Reputable providers generally charge an hourly rate of approximately £200 to £250, or sometimes more, depending on various factors. It’s important to note that the final cost may vary based on the size and complexity of the assessment.
Be cautious of penetration testing providers offering significantly lower prices, as they may rely solely on automated scanners or employ unqualified staff. This can result in low-quality assessments that miss high-risk issues and produce false positives.
Should I Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing as a Part of my ISO 27001 Audit?
Even though penetration tests and vulnerability assessments are not mandatory for ISO 27001 compliance, they offer multiple benefits for achieving industry and regulatory compliance audit goals and enhancing cyber defenses:
- Vulnerability Identification Pentesting helps organizations identify security issues in their systems and networks that malicious hackers might exploit.
- Effort Prioritization and Reduction of Risk Penetration test findings highlight security gaps and expose risks, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts and improve overall security defenses, thereby reducing cyber risks.
- Compliance Regular penetration testing and vulnerability scanning bring organizations closer to meeting ISO 27001 requirements, as well as other standards like AICPA’s SOC 2, PCI DSS, and HIPAA.
- Challenging the Effectiveness of Security Controls Technical security assessments enable organizations to evaluate how well their security controls detect and prevent attacks. This helps identify gaps and weaknesses in their defenses.
- Protect Against Cyber-attacks and Data Breaches Professional penetration tests help organizations anticipate real-life threats by identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers, thus going beyond mere compliance.
- Increased Security Awareness Pen testing serves as a practical learning opportunity, enhancing security awareness and understanding among employees and management, and supporting the business case for increased investments in cyber defense.
How Often Should an ISO 27001 Penetration Test Be Run?
This is generally recommended to be run annually. It’s common for companies to undergo ISO 27001 audits on this basis. Irrespective of the validity of the certificate and appropriately audited controls, continual improvement and auditiing of an organization’s cyber defenses requires regular penetration testing.
What Types Of ISO 27001 Penetration Test Are There?
At any stage of your ISO 27001 ISMS project, penetration testing can be aligned with the requirements most relevant to your organization’s risk landscape. Tests may include:
Network Infrastructure Testing: We thoroughly investigate your network to identify and exploit a wide range of security vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors. This allows us to determine if assets such as data can be compromised, classify the risks to your overall cybersecurity, prioritize vulnerabilities to be addressed, and recommend actions to mitigate identified risks.
Wireless Testing: Unsecured wireless networks can enable attackers to enter your network and steal valuable data. Wireless penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities, quantifies potential damage, and determines appropriate remediation measures.
Application and API Security Review: Software vulnerabilities are commonly exploited by cybercriminals and can be easily introduced by programmers if sanitation among other security protocols have not been considered. We conduct automated and manual penetration tests to assess backend application logic, software, and API source code.
Remote Working Assessment: If your organization is embracing mass remote working for the first time, it’s important to ensure secure implementation. Our custom remote working security assessment ensures your networks, applications, and devices are fully protected.
Web Application Security Testing: Web applications are necessary for business success and are attractive targets for cybercriminals. Our ethical hacking services include penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and flaws in application logic and session management.
Social Engineering: People remain one of the weakest links in an organization’s cybersecurity. Our social engineering penetration test service includes a range of email phishing engagements designed to assess your systems’ and personnel’s ability to detect and respond to simulated attacks.
Mobile Security Testing: With the rise of mobile app usage, companies are increasingly enabling customers to access their services via tablets and smartphones. We perform in-depth mobile application assessments based on the latest development frameworks and security testing tools.
Firewall Configuration Review: Firewall rule sets can quickly become outdated. Our penetration testers detect unsafe configurations and recommend changes to optimize security and throughput.
By integrating these tests, your organization can ensure comprehensive security coverage aligned with ISO 27001 requirements and enhance its overall cybersecurity posture.
Closing Thoughts.
ISO 27001 is an highly valuable resource for businesses aiming to upgrade their information security processes, protect customer data, and demonstrate a robust information security management system with strong controls in place.
Although penetration testing and vulnerability scanning are beneficial for identifying security vulnerabilities and assessing associated risks, they are not mandatory for ISO 27001 compliance. The decision to include penetration testing or vulnerability assessments in your ISO 27001 audit should be based on your organization’s specific risk profile and security objectives.
However, providing an auditor with a comprehensive penetration test report (detailing technical vulnerabilities, mitigation measures, and compensating controls), along with evidence of quarterly vulnerability scans, can significantly bolster confidence in your organization’s information security practices and security controls.
If your organization is seeking a trusted partner for ISO 27001 audit and penetration testing services or other cybersecurity consulting activities, contact our experts at Nelson Douglas today.




No responses yet